XENOFAT: Influence of climatic change and pesticide usage on fatty acids in the food web
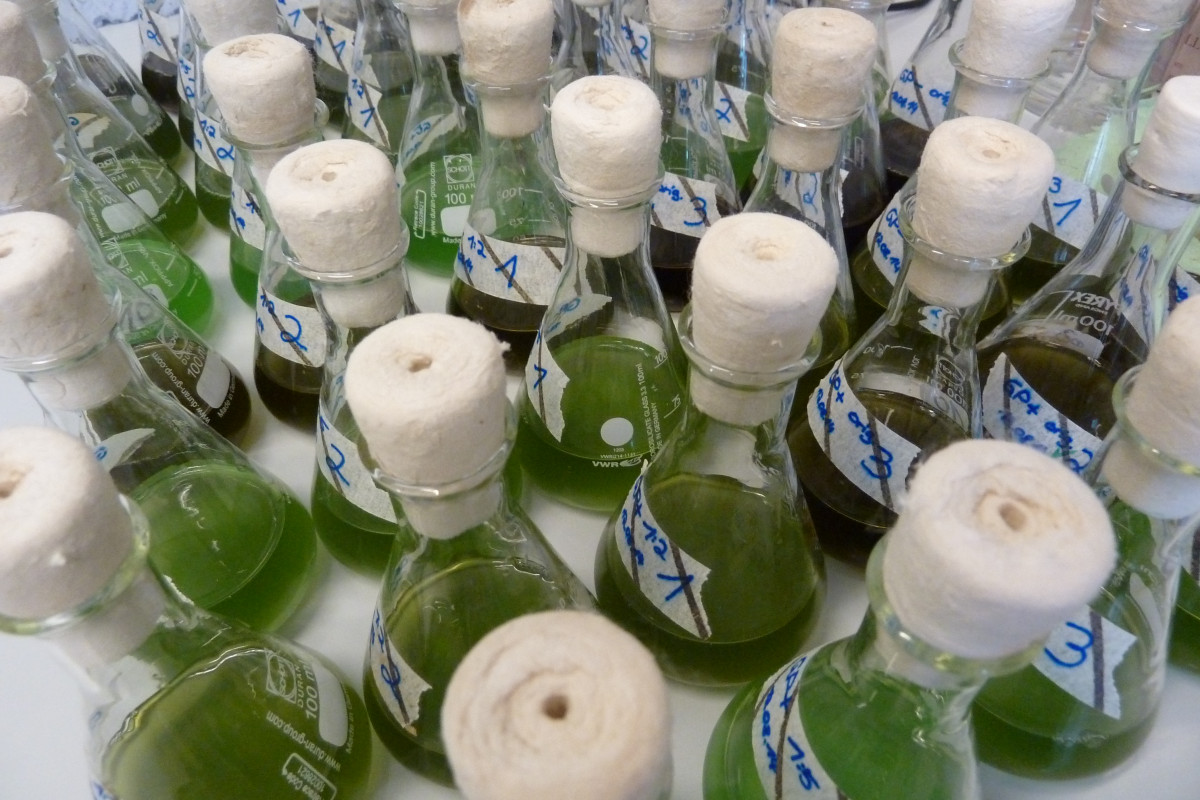
In aquatic systems, essential biomolecules such as fatty acids are produced by phytoplankton and passed on to zooplankton, fish and ultimately humans. Fatty acids fulfil important functions in living organisms - they store energy, are part of the cell membrane and important for brain development. It is not only the quantity of fats, but above all the fatty acid profile that is decisive. This is mainly determined by the primary producers - i.e. phytoplankton - and can only be changed to a limited extent by fish, for example. The fatty acid metabolism of phytoplankton is, however, strongly influenced by environmental factors. Therefore, the rise in temperature due to climate change and the introduction of xenobiotics such as pesticides can have serious consequences for aquatic organisms and us humans.
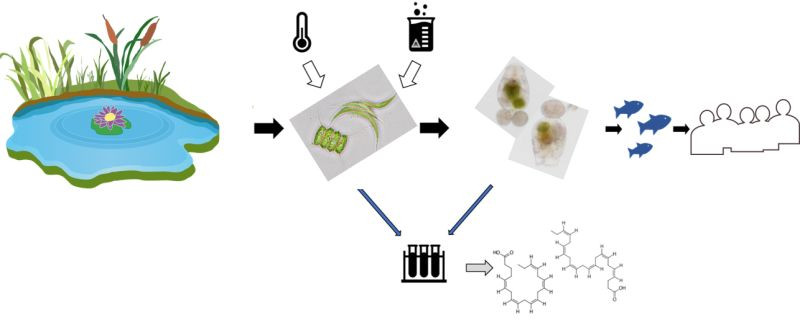
This topic is of great importance for the Waldviertel in Lower Austria with its many carp ponds. Due to the predicted increase in temperature and the accumulation of heavy rainfall events which will increase the amount of xenobiotics entering carp ponds, the issue is becoming even more important. The main aim of this research project is therefore to analyze the effects of temperature increase and pesticides on the nutritional value of organisms in Waldviertel carp ponds. BEST, BOKU IBAM and UT as well as WasserCluster Lunz are involved in the project.
Start of project
2023-06-01 (ongoing)
Supported by
Gefördert von GFF – Gesellschaft für Forschungsförderung Niederösterreich m.b.H., FTI-Projekte Grundlagenforschung: https://calls.einreichsystem.at/calls/fti-projekte-grundlagenforschung/
Projektpartner


BOKU, IBAM: https://boku.ac.at/ifa-tulln/institut-fuer-bioanalytik-und-agro-metabolomics
BOKU, UT: https://boku.ac.at/ifa-tulln/institut-fuer-umweltbiotechnologie/arbeitsgruppen/umweltmikrobiologie
BEST, Area 1.2: https://www.best-research.eu/content/de/kompetenzbereiche/bioraffinerien/biochemische_technologien
WCL, Liptox: https://www.wcl.ac.at/index.php/de/forschung/arbeitsgruppen
Contact

Mario PREIDELT
mario.preidelt@best-research.eu
Area Management

Bernhard DROSG
bernhard.drosg@best-research.eu


