CFD simulation of dust flames
The particle burn-up model developed in sub-area 2.1 is used and further developed, among other things, for the evaluation of the burn-up of dust flames.
CFD simulation of a blow-in dust furnace
The aim of the project is the 3D-CFD simulation of an injection dust furnace in order to be able to investigate the burnout of the dust particles for different performance classes and geometries. Within the scope of the project, the model was extended for the calculation of particle size distributions.
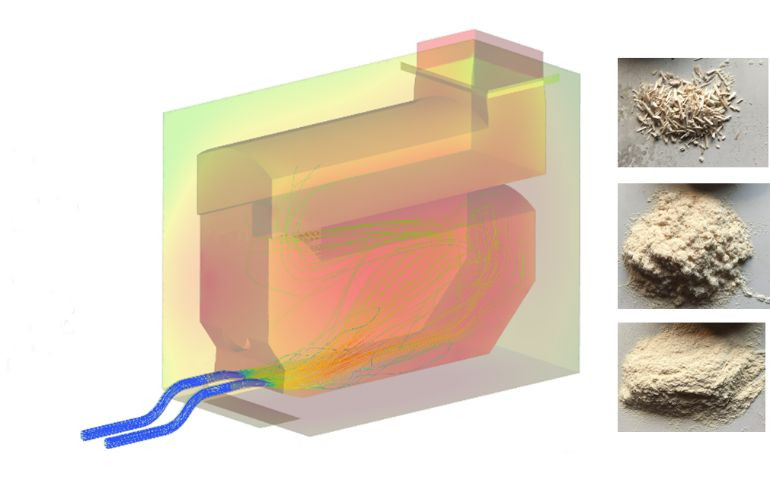
Fig.: Particle paths of wood dust particles during combustion in a blow-in dust furnace, as well as sieve fractions of the wood dust used.
CFD study of a rotary kiln burner for the production of cement
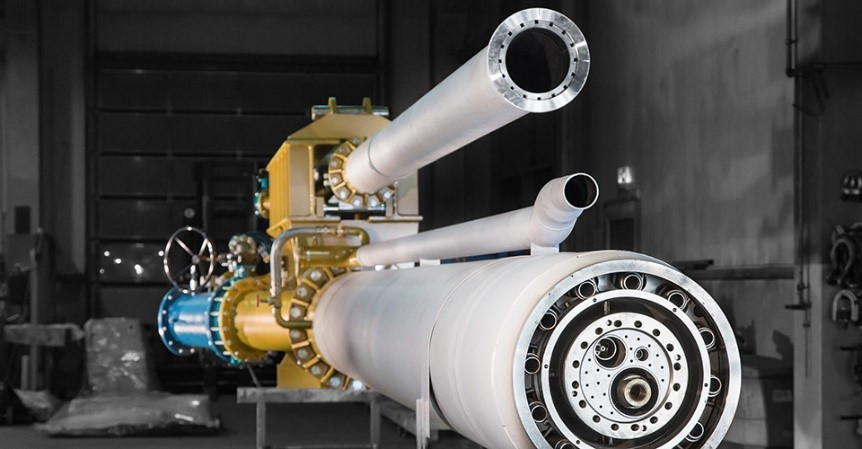
Fig.: Burner tip of a rotary kiln burner from Unitherm Cemcon Feuerungsanlagen GmbH.
Due to the high energy requirements in the production of cement and the associated climate-relevant emissions, increased efforts are being made to further develop the process in terms of materials and energy. A central role in the process chain is played by the rotary kiln burner, which provides the energy for converting the raw materials into clinker with the help of various solid, liquid and gaseous input materials. The burner design essentially determines the quality of the cement, but also the emissions associated with the process.
The aim of the project is to model a rotary kiln burner under typical conditions of the clinker production process. For this purpose, the influence of various geometrical and fluid mechanical burner parameters, such as the coaxial nozzle protrusions at the burner mouth, the speed of the secondary air or the ratio of the burner diameter to the kiln diameter; on the intensity and shape of the flame in the rotary kiln is to be investigated in order to derive measures for optimizations.